How AMOLED Works:
AMOLED uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied, unlike LCD displays that rely on a backlight. Each pixel in an AMOLED display is made up of individual organic LEDs that can emit their own light, meaning no need for a separate backlight.
Key Components:
1. Active Matrix: An "active matrix" refers to the technology that controls the pixels individually, allowing for better responsiveness, faster refresh rates, and more accurate image rendering.
2. Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs): The organic material used in the pixels emits light when an electrical current passes through it. This allows for bright, vibrant colors and deep blacks.
3. Color Filters: Like other displays, AMOLED uses red, green, and blue filters to create the full color spectrum.
Key Features of AMOLED Displays:
True Black Levels:
Each pixel can be turned off completely (because OLED pixels don’t require a backlight), which results in true blacks. This gives AMOLED displays incredible contrast ratios, much higher than LCDs.
Vivid Colors:
AMOLED screens can produce more vibrant and saturated colors due to their ability to independently control each pixel’s brightness and color. This leads to richer, more dynamic visuals.
Energy Efficiency:
1. AMOLED displays are more power-efficient when displaying darker images, because pixels are turned off to render black. However, displaying bright images (especially white backgrounds) can use more power compared to LCDs.
2. This is why devices with AMOLED displays often have a "dark mode" to save battery life.
Wide Viewing Angles:
AMOLED displays generally offer better viewing angles than LCDs. The colors and brightness remain consistent even when viewed from the side.
Thin and Flexible:
Since AMOLED displays do not require a backlight, they can be made thinner and more flexible than LCDs. This makes them suitable for devices with curved or flexible screens, like foldable smartphones or wearables.
Faster Response Times:
AMOLED displays generally have faster response times than LCDs, which makes them better for high-motion content like gaming and video.
Higher Contrast Ratios:
The ability to turn off individual pixels leads to near-infinite contrast ratios. This means bright images pop in a way that’s much more dramatic than what you can get with an LCD.
Common Applications of AMOLED Displays:
Smartphones and Tablets:
AMOLED screens are commonly used in flagship smartphones like the Samsung Galaxy series and Apple’s iPhone (some models). They are favored for their vibrant colors and deep blacks.
Television:
Some high-end TVs, like those from Samsung and LG (e.g., OLED TVs), use OLED technology to deliver exceptional picture quality with rich colors and stunning contrast.
Wearables:
Smartwatches like the Apple Watch and Samsung Galaxy Watch use AMOLED displays to provide sharp, crisp visuals while being energy-efficient.
Laptops and Monitors:
Some premium laptops and monitors feature AMOLED displays for superior color accuracy and contrast, especially useful in creative fields like photography, graphic design, and video editing.
Digital Signage:
AMOLED technology is used in high-end digital signage applications where high contrast and vibrant colors are needed.
Advantages of AMOLED over LCD:
· Superior Black Levels: As mentioned earlier, AMOLED’s ability to turn off pixels results in true blacks, which is a big advantage for contrast.
· Better Color Saturation: AMOLED displays often produce more vibrant and saturated colors compared to LCDs.
· More Flexible: AMOLED panels are thinner, lighter, and can be curved or even rolled, unlike the rigid nature of traditional LCDs.
· Energy Efficiency with Dark Content: AMOLED screens are more power-efficient when displaying dark images, as pixels can be turned off.
Summary:
AMOLED displays offer superior picture quality with stunning contrast, vibrant colors, and true blacks. They are particularly useful for premium devices where display quality is a major selling point. However, potential drawbacks like burn-in and lower brightness in bright environments need to be considered depending on the use case.
Custom AMOLED Solutions for Diverse Applications
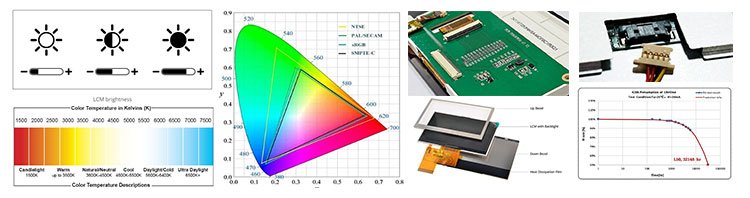
Brightness from 0-3000 for perfect display effect achievement. 100% NTSC makes the vividness of the picture better and the color transition in the picture more natural.
Color Temperature is positive white at around 5500K, warm white (yellowish) at 3500K and also cool white (cold) at 6500K.
Driver circuit with sufficient voltage and current values to meet output requirements and reduce the secondary development cycle.
Heat dissipation for high-brightness products to advance design of reasonable heat dissipation structure.
Power consumption, we increase the brightness without increasing the power consumption.
Cables, Backlighting also requires cables, either through an FPC connected to the LCD's FPC and controlled through a port, or a separate cable that controls it through a connector.LED life reached the standard of 30K hours Min. 50K, 70K, 100K hours are all achievable.
AMOLED Display Touch screen,standard type and customization 
AMOLED Display Driver board/adapter board, standard type and design customization
DEMO board, H-DMl board, other customized board, etc.
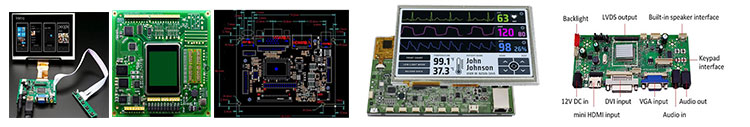
AMOLED Display Embedded Integrated Solution
UART display solution, H-DMl display solution, Window display solution, Android display solution, Raspberry Pi solution, portable secondary screen solution, etc.