Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:

1. Backlight: The screen has a light source (usually LEDs) behind it to illuminate the display.
2. Liquid Crystals: These are tiny molecules that can change their alignment when an electric current is applied. This controls how much light passes through.
3. Color Filters: Red, green, and blue filters are used to create the full color spectrum by mixing these basic colors.
4. Pixels: The screen is made up of thousands or millions of tiny pixels. Each pixel contains liquid crystals that adjust to form the image or text you see.
LCD displays have several features that make them popular for a wide range of applications, from smartphones to TVs. Some of the key features of LCD displays include:
1. Thin and Lightweight
· Compact Design: LCD panels are generally thin and lightweight, which makes them ideal for portable devices like laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
2. Energy Efficiency
· Low Power Consumption: LCDs are more energy-efficient compared to older technologies like CRT (Cathode Ray Tube), especially with LED backlighting, which uses less power than traditional fluorescent backlights.
3. Wide Range of Sizes
· Versatility: LCD technology can be scaled up or down in size to fit various devices, from tiny smartwatches to large TVs or digital signage displays.
4. Sharp and Clear Image Quality
· Resolution: LCDs offer high-resolution images, providing sharp text and clear visuals. Common resolutions include Full HD (1080p), 4K, and even 8K in larger displays.
· Brightness: Many modern LCDs offer high brightness levels, which make them suitable for use in bright environments or outdoor settings.
5. Color Accuracy
· Good Color Reproduction: LCDs, especially those with higher-end IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels, deliver accurate color reproduction with a broad color gamut.
6. Wide Viewing Angles (IPS Panels)
· Improved Viewing Angles: IPS LCDs provide better color consistency and viewing angles compared to standard TN (Twisted Nematic) panels, making them great for devices where you want to see the screen from various angles.
7. No Burn-in Issues
· Screen Longevity: Unlike OLED displays, LCDs do not suffer from burn-in or image retention issues, making them more durable in the long term.
8. Fast Response Time
· Smooth Motion: Many LCDs offer fast response times, making them suitable for gaming and video playback with minimal motion blur.
9. Cost-Effective
· Affordable: LCD displays are typically more affordable than newer display technologies like OLED and microLED, making them the go-to choice for budget-conscious consumers.
10. Customizable Backlighting
· Backlight Control: Some advanced LCDs feature local dimming or full-array backlighting, allowing for improved contrast and deeper blacks, though they still can't match OLED for true black levels.
11. Low to Moderate Contrast Ratio
· Limited Contrast: While LCDs have decent contrast ratios, they still can't achieve the deep blacks that OLED displays can, because they rely on backlighting.
12. Durability and Reliability
· Sturdy Construction: LCD panels are generally durable and less prone to physical damage compared to other types of screens, like older CRT displays.
13. Better for Bright Environments
· Visibility in Sunlight: LCDs, especially with newer technology like high-brightness or anti-glare coatings, tend to perform better in direct sunlight or bright environments than OLEDs.
While LCDs have many great features, they are gradually being surpassed by newer technologies (like OLED and microLED) for high-end displays due to superior contrast ratios and vibrant color rendering. However, LCDs remain a great choice for many everyday applications due to their balance of performance and affordability.

LCD displays are widely used in various applications across multiple industries due to their versatility, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some common applications of LCD displays:
1. Consumer Electronics
Smartphones & Tablets
Laptops & Desktop Monitors
TVs
Digital Cameras
Smartwatches & Fitness Trackers
2. Automotive Displays
Dashboard Screens
Rearview Cameras
Head-up Displays (HUDs)
3. Medical Equipment
Patient Monitors
Diagnostic Devices
Medical Imaging Displays
4. Consumer Appliances
Microwave Ovens
Refrigerators
Washing Machines & Dishwashers
5. Industrial & Commercial Applications
Control Panels
POS (Point of Sale) Systems
Digital Signage
6. Gaming & Entertainment
Video Game Consoles
Arcade Machines
Movie Theaters
7. Aerospace & Military
Avionics Displays
Military Equipment
8. Retail & Advertising
Interactive Kiosks
Billboards
9. Smart Home Devices
Smart Speakers
Home Automation Panels
10. Wearable Technology
Fitness Bands
Smart Glasses
11. Education & Research
E-Boards
Scientific Instruments
12. Security & Surveillance
CCTV Monitors
Access Control Systems
13. Transportation
Bus and Train Displays
Flight Information Displays
14. Advertising & Information Displays
Public Information Displays
Digital Menu Boards
In summary, the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of LCD displays make them essential in numerous industries, offering clear, vibrant, and reliable visual output across a wide variety of applications.
Custom LCD Solutions for Diverse Applications
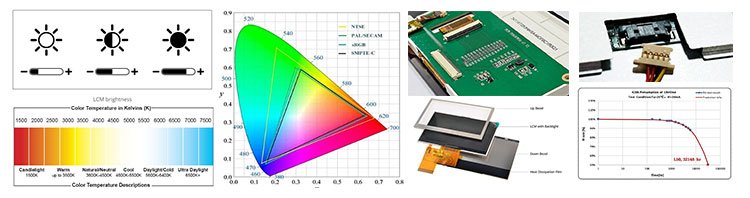
Brightness from 0-3000 for perfect display effect achievement. 100% NTSC makes the vividness of the picture better and the color transition in the picture more natural.
Color Temperature is positive white at around 5500K, warm white (yellowish) at 3500K and also cool white (cold) at 6500K.
Driver circuit with sufficient voltage and current values to meet output requirements and reduce the secondary development cycle.
Heat dissipation for high-brightness products to advance design of reasonable heat dissipation structure.
Power consumption, we increase the brightness without increasing the power consumption.
Cables, Backlighting also requires cables, either through an FPC connected to the LCD's FPC and controlled through a port, or a separate cable that controls it through a connector.LED life reached the standard of 30K hours Min. 50K, 70K, 100K hours are all achievable.
LCD Display Touch screen,standard type and customization 
LCD Display Driver board/adapter board, standard type and design customization
DEMO board, H-DMl board, other customized board, etc.
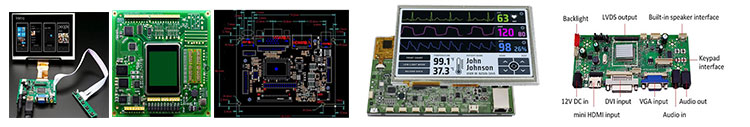
LCD Display Embedded Integrated Solution
UART display solution, H-DMl display solution, Window display solution, Android display solution, Raspberry Pi solution, portable secondary screen solution, etc.