Automotive Display Features

1. Display Type and Technology
· LCD (Liquid Crystal Display): Common in most vehicles for both infotainment and instrument clusters, providing a good balance of quality and cost.
· OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode): Offers deeper blacks and better contrast, making it ideal for high-end or luxury vehicles. OLED displays are more energy-efficient and can be curved to fit various dashboard shapes.
· LED Backlighting: Often used to enhance the brightness and contrast of LCD screens, improving visibility under sunlight.
· TFT (Thin Film Transistor): Used for higher-resolution displays and faster refresh rates, typically in digital instrument clusters and advanced navigation systems.
2. Size and Aspect Ratio
· Screen Size: Automotive displays range from 7 inches (common for mid-range cars) to 12-15 inches (premium or luxury vehicles). Larger screens are used for infotainment, navigation, and more detailed driver information.
· Aspect Ratio: The standard 16:9 aspect ratio is common, but increasingly, 16:10 or 21:9 ultrawide displays are used to provide more screen space for multitasking, such as navigation and media simultaneously.
3. Resolution and Clarity
· Full HD (1920x1080) is common for many automotive applications, providing crisp, clear visuals for navigation, media, and backup cameras.
· Higher Resolutions (QHD or 4K) may be found in high-end vehicles, providing extra detail for rearview or surround-view cameras, or premium media experiences.
4. Touchscreen vs. Non-Touchscreen
· Touchscreen Displays: Most modern vehicles use touchscreen interfaces for infotainment, navigation, and vehicle controls. These should be responsive, intuitive, and easy to use while driving.
· Non-Touchscreen: Some systems rely on physical buttons, knobs, or touchpads for control. Non-touch displays may be used for critical functions like the digital instrument cluster to reduce distractions.
· Haptic Feedback: Some systems combine touchscreens with haptic feedback (vibration), providing tactile responses to user inputs, improving usability.
5. Brightness and Anti-Glare
· High Brightness: Displays need to be bright enough to maintain visibility in direct sunlight, particularly for navigation or rearview cameras.
· Anti-Glare Coating: Prevents reflections and improves clarity, especially for touchscreens, which can be prone to glare.
6. Wide Viewing Angles
· Automotive displays, especially those in the center console or dashboard, need to have wide viewing angles to ensure that drivers and passengers can clearly view the screen from various positions.
7. Glove Compatibility
· Displays used in cars should be responsive even when using gloves, especially in colder climates where drivers are more likely to wear gloves. This ensures usability in all conditions.
8. Connectivity
· Bluetooth & Wi-Fi: Essential for smartphone integration (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto), streaming music, or making hands-free calls.
· USB Ports: For device charging and media connection.
· HDMI / DisplayPort: Some advanced systems, especially rear-seat entertainment displays, may require HDMI ports for media input.
· Wireless Connectivity: Integration with smartphones and in-car systems (e.g., remote updates, data streaming).
9. Multimedia Integration
· Apple CarPlay & Android Auto: These features allow drivers to seamlessly connect their smartphones to the infotainment system for navigation, media, and hands-free calls.
· Media Sources: Integration with USB drives, Bluetooth audio, FM/AM radio, satellite radio, and streaming apps (e.g., Spotify, YouTube).
· Voice Control: Advanced voice recognition for hands-free control of the infotainment system, navigation, and even car settings (e.g., temperature, seat adjustments).
10. Multi-Function Display
· Infotainment and Navigation: Many automotive displays combine multiple functions, such as infotainment (media, radio), navigation (maps, route guidance), and vehicle diagnostics (engine status, tire pressure, fuel efficiency).
· Driver Assistance Systems: Displays may show features like lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and surround-view camera systems. These require high clarity and quick response times.
· Heads-Up Display (HUD): Some vehicles include a HUD that projects key information onto the windshield, allowing the driver to access critical data without looking away from the road.
11. Customizable Interface
· Displays should allow for customizable settings so that drivers can adjust the layout or information shown on the screen (e.g., showing media info alongside navigation or allowing shortcuts for frequently used functions).
12. Vehicle Integration
· The display should integrate seamlessly with the vehicle’s control systems, including climate control, seating adjustments, and vehicle settings.
· Advanced displays may offer gesture control or eye-tracking for more intuitive, hands-free operation.
13. Durability
· Temperature Resistance: Automotive displays should withstand a wide range of temperatures (e.g., hot sun in summer or freezing temperatures in winter).
· Shock and Vibration Resistance: Displays in vehicles must be durable enough to handle vibrations and impacts, especially in off-road or heavy-duty vehicles.
· Scratch Resistance: Given the likelihood of users interacting with the display frequently, a scratch-resistant surface is essential.
14. Safety Features
· Rearview and Surround-View Cameras: Many displays serve as rearview monitors or part of a surround-view system to help with parking or driving in tight spaces.
· Backup Assist and Collision Avoidance: Some systems integrate collision warning or automatic emergency braking notifications into the display.
· Driving Mode Displays: Some vehicles have modes (e.g., sport, eco, comfort) that change the display configuration or color scheme for improved visibility and driving experience.
15. Climate and Environmental Considerations
· Temperature Adaptability: Automotive displays must work well in extreme conditions, from heat in the summer to cold in the winter.
· Sunlight Readability: Display technologies like ambient light sensors or transflective displays enhance visibility in direct sunlight.
16. Customization and Branding
· Some car manufacturers allow brand-specific themes and custom graphics to be integrated into the display system, creating a unique user experience that aligns with the car's design language.
17. Advanced Features
· Augmented Reality (AR): Some high-end systems are starting to incorporate AR for navigation (e.g., overlaying directional arrows on live video feed from the camera).
· AI Integration: Advanced systems may feature artificial intelligence to personalize driving or media preferences, and even adjust settings based on driver behavior or preferences.
· Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Automotive displays that support OTA updates can receive firmware and software updates automatically, ensuring that the system stays up-to-date without needing a visit to the dealership.
18. Cost and Value
· Budget-Friendly: Entry-level vehicles may feature simpler displays with basic functionality (e.g., a smaller, non-touch screen for radio and climate control).
· Premium Features: High-end vehicles tend to offer larger, more integrated, and more customizable displays with advanced features like 3D navigation, high-definition cameras, and premium sound systems.

Automotive Display Custom LCD Solutions for Diverse Applications
Brightness from 0-3000 for perfect display effect achievement. 100% NTSC makes the vividness of the picture better and the color transition in the picture more natural.
Color Temperature is positive white at around 5500K, warm white (yellowish) at 3500K and also cool white (cold) at 6500K.
Driver circuit with sufficient voltage and current values to meet output requirements and reduce the secondary development cycle.
Heat dissipation for high-brightness products to advance design of reasonable heat dissipation structure.
Power consumption, we increase the brightness without increasing the power consumption.
Cables, Backlighting also requires cables, either through an FPC connected to the LCD's FPC and controlled through a port, or a separate cable that controls it through a connector.
LED life reached the standard of 30K hours Min. 50K, 70K, 100K hours are all achievable. 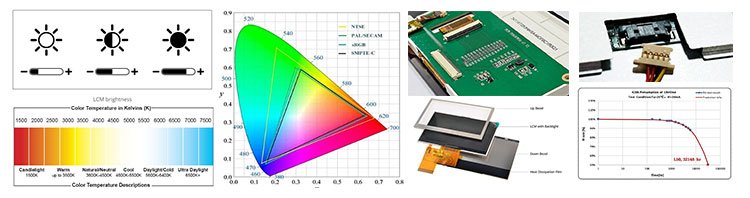
Automotive Display Touch screen,standard type and customization

Automotive Display Driver board/adapter board, standard type and design customization
DEMO board, H-DMl board, other customized board, etc.
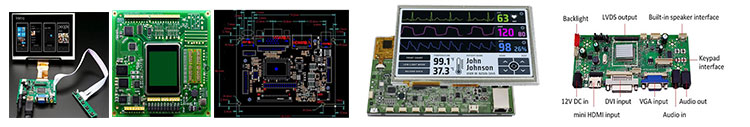
Automotive Display Embedded Integrated Solution
UART display solution, H-DMl display solution, Window display solution, Android display solution, Raspberry Pi solution, portable secondary screen solution, etc.
