Size
Resolution
Interface
Features
Type
Value Added
Model
Datasheet/Quote
0.23" Thermal image scape EVF display
640x400
TTL , 51 pins FPC
2000cd/m² 60Hz
Micro-OLED
AV / HDMI
ECX336BF
Get A Quote
0.23' Thermal image scape EVF display
640×400
RGB
3000cd/m²
Micro-OLED
AV / HDMI
ECX336CN
Get A Quote
0.26" Thermal image scape EVF display
640x480
/
1000 cd/m² 16.7M color
Micro-OLED
DEMO
LSVGA026FC
Get A Quote
0.32" Thermal image scape EVF display
800×600
I2C+RGB and MIP
2000cd/m² / 4000cd/m² / 120HZ
Micro-OLED
Type-C
SY032WEM01
Get A Quote
0.39" Thermal image scape EVF display
1024×768
RGB 61pin FPC
300cd/m²
Micro-OLED
DEMO
ET04122A
Get A Quote
0.39" Thermal image scape EVF display
1024×768
RGB 45pins connector
1500cd/m²
Micro-OLED
DEMO
ET02111A
Get A Quote
0.39" Thermal image scape EVF display
1024x768
RGB 61pin FPC
300cd/m²
Micro-OLED
AV / HDMI
ECX334AF-6
Get A Quote
0.39" Thermal image scape EVF display
1024×768
Sub-LVDS
1000 cd/m²
Micro-OLED
AV / HDMI
ECX334C
Get A Quote
0.39" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
MIPI 60pins connector
300cd/m² 90Hz -40 ~ 85 °C
Micro-OLED
Type-C
VX039-FHP-NH0
Get A Quote
0.49" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
MIPI 40pins connector
1800cd/m² 90Hz -40 ~ 80 °C
Micro-OLED
Type-C
SY049WDM02
Get A Quote
0.49" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920x1080
MIPI 40pins connector
3000cd/m² 90Hz
Micro-OLED
Type-C
SY049LDM01
Get A Quote
0.49" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
MIPI 40pins connector
20000cd/m² 90Hz green
Micro-OLED
Type-C
SY049LDM02
Get A Quote
0.49" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
MIPI 40pins connector
300cd/m² 60Hz
Micro-OLED
Type-C
VX049FHP-NH0
Get A Quote
0.49" Thermal image scape EVF display
1280×720
/
1500cd/m² 120HZ -40 ~ 65 °C
Micro-OLED
DEMO
LS720P049FC
Get A Quote
0.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1600x1200
Sub-LVDS
1000cd/m²
Micro-OLED
AV / HDMI / Micro HDMI
ECX339A
Get A Quote
0.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1600x1200
MIPI (4 data lanes) , 60 pins
1000cd/m² 120Hz
Micro-OLED
DEMO
VX050U0P-NH0
Get A Quote
0.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1280x960
LVDS 60pin FPC
1000cd/m² 120Hz
Micro-OLED
AV / HDMI / Micro HDMI
ECX337A
Get A Quote
0.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
800x600
Parallel/Serial , Connector
300cd/m² 3D
Micro-OLED
DEMO
VX050S0M-NH1
Get A Quote
0.57" Thermal image scape EVF display
1600×1200
MIPI
1800cd/m² 90Hz
Micro-OLED
DEMO
SY057WAM01
Get A Quote
0.6" Thermal image scape EVF display
1280×1024
40 pins Parallel RGB
1500 cd/m² 3D -40 ~ 65 °C
Micro-OLED
DEMO
SXGA060SG
Get A Quote
0.6" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
50 pins MIPI (4 data lanes)
6000 cd/m² 120hz Reverse
Micro-OLED
DEMO
SY060LDM01
Get A Quote
0.6" Thermal image scape EVF display
800×600
RGB 40pins connector
3000cd/m²
Micro-OLED
DEMO
ET03111A
Get A Quote
0.62" Thermal image scape EVF display
1728x1368
MIPI 81pin FPC
1800cd/m² 90Hz
Micro-OLED
DEMO
SY062WAM01
Get A Quote
0.71" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
MIPI 50pins connector
500cd/m² 90HZ
Micro-OLED
DEMO
ET01121A
Get A Quote
0.71" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
MIPI 50pins connector
300cd/m² 90Hz 30 ~ 70 °C
Micro-OLED
HDMI
VX071FHM-NH2
Get A Quote
0.71" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
LVDS 81pin FPC
3000cd/m² 60Hz
Micro-OLED
AV / HDMI / Type-C
ECX335SN-6
Get A Quote
0.71" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1080
Mini LVDS
500cd/m² 60Hz
Micro-OLED
AV / HDMI / Type-C
ECX335B
Get A Quote
0.72" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920×1200
MIPI 61pin FPC
2000cd/m² 60Hz
Micro-OLED
DEMO
SY072WCM02
Get A Quote
0.83" Thermal image scape EVF display
2560×1440
MIPI 81pin FPC
1800cd/m² 90Hz
Micro-OLED
DEMO
SY083WAM01
Get A Quote
0.96" Thermal image scape EVF display
1400x1050
Parallel/Serial+ I²C
20000cd/m² green
Micro-OLED
DEMO
ET05100
Get A Quote
1.03" Thermal image scape EVF display
2560x2560
MIPI 81pin FPC
1800cd/m² 90Hz
Micro-OLED
HDMI
SY103WAM01
Get A Quote
1.03" Thermal image scape EVF display
2560×2560
MIPI 81pin FPC
20000cd/m² 90Hz green
Micro-OLED
HDMI
SY103WAM10
Get A Quote
1.35" Thermal image scape EVF display
3552x3840
MIPI
1200cd/m² 90HZ
Micro-OLED
DEMO
VX135KDP-NM2
Get A Quote
1.9" Thermal image scape EVF display
1600x1200
MIPI 50pins connector
1000cd/m² 120HZ
ADS TFT-LCD
DEMO
VS019U0M-NH0-DKP0
Get A Quote
2.1" Thermal image scape EVF display
1600x1600
MIPI 24pins connector
480cd/m² 90HZ
ADS TFT-LCD
HDMI
VS021XRM-NW0-6KP0
Get A Quote
2.1" Thermal image scape EVF display
1600x1600
MIPI 24pins connector
500cd/m² 90HZ
IPS TFT-LCD
HDMI
LPM021M528C
Get A Quote
2.2" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920x1920
MIPI C-phy (2 ch, 3 data lanes)
580cd/m² 90HZ
LTPS TFT-LCD
HDMI
LPM022M857B
Get A Quote
2.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1440×1600
MIPI 24pins connector
150cd/m² 90HZ
ADS TFT-LCD
HDMI
VS025ZSM-NV0-69P0
Get A Quote
2.6" Thermal image scape EVF display
2160×2160
45 pins MIPI C-ph
700cd/m² 90HZ -40 ~ 85 °C
LTPS TFT-LCD
DEMO
VS026C4T-NH0-69P0
Get A Quote
2.9" Thermal image scape EVF display
2160×2160
MIPI 51pins FPC
100cd/m² 90HZ
SFR TFT-LCD
HDMI
LS029B3SX06A
Get A Quote
2.9" Thermal image scape EVF display
2160x2160
MIPI 51pin FPC
150cd/m² 90HZ
IPS TFT-LCD
HDMI
LPM029M483B
Get A Quote
3" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
380cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET030WV02-R
Get A Quote
3.2" Thermal image scape EVF display
2880x2880
MIPI 70pins connector
190cd/m² 90HZ MINI LED
HADS TFT-LCD
DEMO
VS032B3M-NA1-6KP0
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
Parallel Data
/
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
LS035Q7DD01
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
Parallel/Serial
300cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TM035KDH03-79
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
/
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET035QV10-TT
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
400cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET035WV01-Z
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
1000cd/m2,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET035HV02-HT
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
1000cd/m2,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET035HV02-HT
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
640×480
MIPI
450cd/m2,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET035VG04-T
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
640×480
TTL
650cd/m2,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET035VG02-T
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
350cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TM035KDGP01-00
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
430cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET035HD01-R
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
480×640
MIPI
200cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET035VG02-R
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
480×640
MIPI
900cd/m2
LCM
Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
COM35H3P70ULC
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
480×640
TTL
350cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TM035WDHG03
Get A Quote
3.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1440×1600
MIPI
165 cd/m² 90HZ
AM-OLED
DEMO
U349QLN01.0
Get A Quote
3.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1440×1600
MIPI
MIPI 24pins connector
200cd/m² 90HZ
ADS TFT-LCD
HDMI
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
480×640
TTL
265cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM35H3R14UTC
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
480×640
TTL
330cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM35H3R12ULC
Get A Quote
3.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1440×1600
MIPI 24pins connector
200cd/m² 90HZ
ADS TFT-LCD
HDMI
VS035ZSM-NW0-69P0
Get A Quote
3.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
600cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM35H3P58ULC
Get A Quote
3.6" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
1024×768
MIPI
900cd/m2,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
QV036X0M-T40
Get A Quote
4.1" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
500cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM41H4P21ULC
Get A Quote
4.1" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
TTL
400cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM41H4P23UTC
Get A Quote
4.1" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
500cd/m2,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET041HD01-T
Get A Quote
4.4" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
320×240
SPI
/
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
LS044Q7DH01
Get A Quote
4.4" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
550cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET044HD02-R
Get A Quote
4.7" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
400cd/m2,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TM046JDHP01-30
Get A Quote
4.7" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
400cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET047HD01-T
Get A Quote
4.8" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
300cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM48H4P03ULC
Get A Quote
4.8" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
480cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM48H4P07ULC
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
400cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM50H5N17ULC
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
600cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TM050JDHG33-01
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
640×480
TTL
250cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ZJ050NA-08C
Get A Quote
5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
1200cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET050FH10-T
Get A Quote
5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
TTL
380cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET050VG01-ZK
Get A Quote
5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
720×1280
MIPI
950cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET050HD01-A
Get A Quote
5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
720×1280
MIPI
400cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COM50H5N17ULC
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
950cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET050HD01-A
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
TTL
400cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET050HD20-K
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
350cd/m2
OLED
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET050HD06-Z
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
640×480
TTL
600cd/m2,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX13D200VM5BAA
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
640×480
LVDS
600cd/m2,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX13D202VM5BAA
Get A Quote
5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
LVDS
350cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET050HD10-TT
Get A Quote
5.2" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
1200cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET052FH01-TT
Get A Quote
5.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920x3664
MIPI 60pins connector
100cd/m² 90HZ
CG-Silicon
DEMO
LS055B3SX04Z
Get A Quote
5.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
2160x3840
MIPI 60pins connector
100cd/m² 90HZ
ADS TFT-LCD
HDMI
VS055QUM-NH0-6KP1
Get A Quote
5.5" Handheld Thermal Imager Display
720×1280
MIPI
300cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
E555HBM2
Get A Quote
5.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
2000cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET055WU06-TT
Get A Quote
5.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
720×1280
MIPI
1000 cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET055HD11-T
Get A Quote
5.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
720×1280
MIPI
300cd/m²
AMOLED
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
E555HBM2
Get A Quote
5.5" Thermal image scape EVF display
1920x3664
MIPI 60pins connector
120cd/m² 120HZ dual
IPS TFT-LCD
DEMO
LPM055M493F
Get A Quote
5.6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
TTL
1400cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET056VG01-ST
Get A Quote
5.7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
TTL
1000 cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX14D203VM0BAA
Get A Quote
5.7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
TTL
1000 cd/m²,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TM057QDHG10-00
Get A Quote
5.7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
TTL
700cd/m2,89/89/89/89,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
G057VN01 V220
Get A Quote
5.7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
LVDS
800cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX14D204VM0BAA
Get A Quote
5.7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
MIPI
1500cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET057VG02-Z
Get A Quote
6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
800cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET060FH02-TT
Get A Quote
6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
800ced
Get A Quote
6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
800ced
Get A Quote
6.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
LVDS
800cd/m2,89/89/89/89,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
G065VN01 V221
Get A Quote
6.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
TTL
1200cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P0650VGF1MA01
Get A Quote
6.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
LVDS
1200cd/m2,88/88/88/88,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P0650VGF1MA00
Get A Quote
6.9" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
750cd/m2,-40~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
C070EAN03.0
Get A Quote
6.9" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
750cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
M069AWA1 R0
Get A Quote
7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1200×1920
MIPI
1500cd/m²,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET070WU14-TT
Get A Quote
7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
1000cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
M070AWAD R0
Get A Quote
7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1200×1920
MIPI
1500cd/m²,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET070WU14-TT
Get A Quote
7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1200×1920
MIPI
1500cd/m²,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET070WU14-TT
Get A Quote
7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1200×1920
MIPI
2000cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ZD070VA-01A
Get A Quote
7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
2000cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET070FH01-RT
Get A Quote
7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1200cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-40~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX18D200VM0EAA
Get A Quote
7" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
1000 cd/m²,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET7D0023
Get A Quote
7.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1080×1920
MIPI
700cd/m²
AMOLED
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET071AM01-HT
Get A Quote
8" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
750cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
DJ080IA-11A
Get A Quote
8" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
1200cd/m2,88/88/88/88,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
A0800WXF1MB00
Get A Quote
8" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
900cd/m2,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
C080EAN04.3
Get A Quote
8" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
800cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
AV080HDM-N19
Get A Quote
8" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1200
LVDS
2000cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET080WWV-R1
Get A Quote
8.4" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
LVDS
900cd/m2,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
NL6448BC26-27F
Get A Quote
8.4" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
TTL
900cd/m2,88/88/88/88,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P0840VGF1MA00
Get A Quote
9" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
850cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
DD090IA-05A
Get A Quote
9" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
800cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-40~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
HSD090JHW1-D10
Get A Quote
10.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1200
LVDS
800cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX26D202VM0BAA
Get A Quote
10.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1100cd/m2,85/85/30/30,-40~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COG-VLSZT115-01
Get A Quote
10.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1280×720
LVDS
750cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
DJ101IA-07A
Get A Quote
10.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
720×1280
MIPI
900cd/m2
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET101HD01-YS
Get A Quote
10.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1200
LVDS
1400cd/m2,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
C101UAN01.0
Get A Quote
10.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1200
MIPI
1500cd/m²,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET101WU02-ZK
Get A Quote
10.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1200
eDP
1000 cd/m²
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
GV101WUM-N40
Get A Quote
10.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1200
LVDS
2000cd/m²,85/85/85/85,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET101WU01-R
Get A Quote
10.2" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1300cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-40~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX26D208VM0AAA
Get A Quote
10.4" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
LVDS
1500cd/m²,80/60/80/80,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TCG104VGLPCANN-AN40
Get A Quote
10.4" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
LVDS
900cd/m2,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
NL6448BC33-71C
Get A Quote
10.4" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
640×480
TTL
900cd/m2,88/88/88/88,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P1040VGF1MA00
Get A Quote
11.6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1200cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-40~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX29D200VM0AAA
Get A Quote
12.1" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1200
LVDS
1000 cd/m²,89/89/89/89
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET121WU01-ZX
Get A Quote
12.8" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
700cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
HSD128JUW1-A10
Get A Quote
13.3" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
3840×2160
eDP
2000cd/m²,89/89/89/89
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET133UH01-RT
Get A Quote
15.6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
eDP
1500cd/m²,88/88/88/88,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
NL192108BC18-06F
Get A Quote
15.6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
3840×2160
eDP
1000 cd/m²,89/89/89/89
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
NE156QUM-NM1
Get A Quote
15.6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1500cd/m²,85/85/85/85,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
TX40D202VM0BAA
Get A Quote
15.6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1000 cd/m²,88/88/88/88,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P1560FHF2MA00
Get A Quote
15.6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1000 cd/m²,89/89/89/89,-30~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
G156HAN04.0
Get A Quote
15.6" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1200cd/m2,89/89/89/89,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
G156HCE-LH1
Get A Quote
17" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1200
LVDS
1000 cd/m²,88/88/88/88
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET170WU01-Z
Get A Quote
17.3" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
eDP
1200cd/m2,88/88/88/88,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P1730FHF1MA10
Get A Quote
17.4" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1200×1920
LVDS
950cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-40~85°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
COG-PVLSHT022-01
Get A Quote
18.4" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
3840×2160
eDP
1000 cd/m²,85/85/85/85
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
EV184QUM-N80
Get A Quote
18.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
3840×2160
eDP
1400cd/m2,88/88/88/88
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P1850UHF1MA00
Get A Quote
18.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
eDP
1800cd/m²,89/89/89/89,-30~70°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
G185HAN01.4
Get A Quote
18.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1000cd/m2,85/85/85/85,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
ET185FH21-K
Get A Quote
21.5" Vessel thermal imaging system Display
3840×2160
eDP
1400cd/m2,88/88/88/88
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P2150UHF1MA00
Get A Quote
21.5" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1400cd/m2,89/89/89/89,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
G215HCJ-LH1
Get A Quote
23.8" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
3840×2160
eDP
1300cd/m2,88/88/88/88
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
P2380UHF1MA00
Get A Quote
23.8" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1000 cd/m²,88/88/88/88,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
G238HCJ-LH1
Get A Quote
24" Vehicle/Vessel thermal imaging system Display
1920×1080
LVDS
1500cd/m²,85/85/80/80,-30~80°C
LCM
Customize Brightness, Touch, Surface & Embeded
G240HVN01.0
Get A Quote
Infrared Night Vision Display
Infrared night vision displays are typically used in specialized applications like military, security, and certain advanced gaming or simulation systems. These displays utilize infrared technology to allow users to see in low-light or completely dark environments. Here are the key features to look for in an infrared night vision display:
1. Infrared Sensor Type
· Active IR: Uses an infrared light source (such as infrared LEDs) to illuminate the surroundings, with the sensor capturing the reflected infrared light. This type works well in complete darkness.
· Passive IR: Relies on ambient infrared radiation from natural sources, like heat from living organisms, to create an image. These displays typically have lower resolution and less range compared to active IR systems but are excellent for observing natural heat signatures.
2. Resolution
· Resolution in night vision displays is typically lower than traditional displays. This is because the technology behind infrared imaging tends to be less detailed than visible light imaging.
· Higher resolution models provide clearer images, but even with lower resolutions, many IR systems provide good performance for basic surveillance or navigation in low-light conditions.
3. Field of View (FOV)
· Wide FOV: A larger field of view allows you to cover more area in the dark, which is especially helpful for surveillance, hunting, or security operations. A wider FOV typically comes at the cost of a slightly reduced magnification range.
· Zoom: Some night vision displays allow you to zoom in or out to focus on distant objects.
4. Display Type
· LCD/LED: Most infrared night vision displays use an LCD or LED screen to show the infrared image. These screens can be designed with high contrast and a dark background for better viewing in the dark.
· OLED: Higher-end systems might use OLED displays for better contrast, deeper blacks, and better visibility in dark environments.
5. Infrared Light Source
· Some night vision systems come with built-in IR illuminators that emit infrared light to help improve visibility in total darkness. This is essential when there's no ambient infrared radiation (like starlight or heat sources).
· Adjustable IR levels: This feature allows you to control the brightness of the infrared light, so you don't wash out the image or make it too bright.
6. Range and Detection Distance
· Effective Range: The distance at which the system can detect objects using infrared light. High-quality infrared systems can detect heat signatures or objects at distances ranging from 100 feet to several miles, depending on the system.
· Detection Angle: The angle at which the infrared sensors can detect and display images. Wider angles are great for surveillance or situational awareness.
7. Contrast and Brightness Control
· The ability to adjust contrast and brightness can help improve visibility, especially in varying lighting conditions. Many systems have manual or automatic adjustments for optimal viewing.
8. Low Light and Full Dark Performance
· The ability to see in low light (ambient moonlight, streetlights) and complete darkness is crucial. Some systems excel in one area more than the other, depending on the design of the infrared sensor and light source.
· Auto-Gain Control (AGC): This helps maintain a clear image by automatically adjusting the sensitivity to light and dark conditions, preventing overexposure or too much darkness in the image.
9. Power Source and Battery Life
· Infrared systems often use rechargeable batteries or replaceable power sources. Battery life can be crucial, especially for extended operations. Long-lasting batteries (often 6-10 hours) are preferred for field use.
· Some systems may offer low-power modes to extend battery life while still providing essential infrared performance.
10. Portability
· Some infrared night vision displays are portable (e.g., handheld devices), while others are built into stationary systems for surveillance purposes. Portability is important for personal or tactical use, where you need to move and operate the system in different environments.
11. Durability and Weather Resistance
· Many infrared night vision systems are weatherproof or water-resistant, especially for military or security applications. Look for systems that can withstand harsh environmental conditions like rain, snow, and dust.
· Systems designed for field use should also be shock-resistant to prevent damage in rugged terrain.
12. Recording and Connectivity
· Some infrared systems come with built-in recording capabilities, allowing you to capture images or video for later review. This is particularly useful for security purposes.
· Wi-Fi/Bluetooth: Some models allow you to connect the display to external devices like smartphones, tablets, or computers for remote viewing or data storage.
13. Size and Weight
· The size and weight of the display can affect its portability and usability. Compact and lightweight designs are typically used for handheld devices, while larger systems may offer more advanced features at the expense of mobility.
14. Image Processing Features
· Digital Zoom: Allows for zooming into specific areas of the scene.
· Thermal Fusion: Some advanced systems combine thermal imaging with visible light or enhanced infrared, helping to highlight key features or figures in the environment.
· Edge Detection and Image Enhancement: Some systems use algorithms to enhance image clarity, especially when objects are hard to differentiate due to low contrast.
15. Cost and Intended Use
· Budget Systems: Typically lower-resolution and fewer features, suitable for basic nighttime use.
· High-end Systems: Offer superior resolution, longer detection ranges, better image processing, and more advanced features like thermal fusion or multi-spectral viewing.
Infrared night vision displays have a wide range of applications across different fields due to their ability to enhance vision in low-light and complete darkness. These systems work by using infrared sensors and displays to capture and present images based on infrared radiation (heat), allowing users to "see" in environments that are invisible to the naked eye. Here are some of the key applications:

1. Military and Tactical Use
· Surveillance
Navigation
Search and Rescue
Sniper Operations
Covert Operations
2. Security and Surveillance
Home Security
Perimeter Monitoring
CCTV and Law Enforcement
3. Wildlife Observation and Research
Wildlife Tracking
Hunting
4. Aviation and Aerospace
Pilot Vision Enhancement
Helicopters and Drones
5. Law Enforcement and Border Patrol
Nighttime Surveillance:
Border Patrol
6. Automotive and Driver Assistance Systems
Night Driving Assistance
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
7. Search and Rescue Operations
Disaster Response
Mountain and Wilderness Rescues
8. Archaeology and Exploration
Archaeological Surveys
Cave Exploration:
9. Industrial Inspections
Electrical Systems Inspection
Oil and Gas
Building and Infrastructure Inspections
10. Military Simulations and Training
Tactical Training
Virtual and Augmented Reality
11. Science and Medical Applications
Thermal Imaging in Medicine:
Biological Research
12. Entertainment and Gaming
Simulation and VR
Theme Parks and Haunted Attractions
Overall, infrared night vision displays have broad applications that span across safety, security, research, exploration, and entertainment. Their ability to provide visibility in total darkness makes them essential tools in environments where regular vision would be inadequate or impossible.
Infrared Night Vision Display Custom LCD Solutions for Diverse Applications
Brightness from 0-3000 for perfect display effect achievement. 100% NTSC makes the vividness of the picture better and the color transition in the picture more natural.
Color Temperature is positive white at around 5500K, warm white (yellowish) at 3500K and also cool white (cold) at 6500K.
Driver circuit with sufficient voltage and current values to meet output requirements and reduce the secondary development cycle.
Heat dissipation for high-brightness products to advance design of reasonable heat dissipation structure.
Power consumption, we increase the brightness without increasing the power consumption.
Cables, Backlighting also requires cables, either through an FPC connected to the LCD's FPC and controlled through a port, or a separate cable that controls it through a connector.LED life reached the standard of 30K hours Min. 50K, 70K, 100K hours are all achievable. 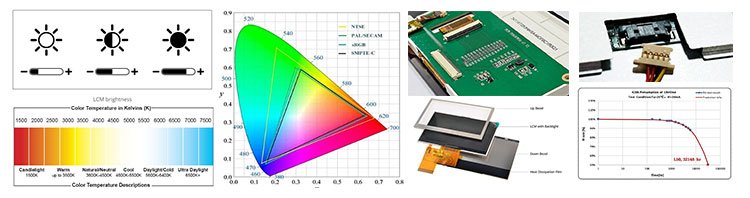
Infrared Night Vision Display Touch screen,standard type and customization 
Infrared Night Vision Display Driver board/adapter board, standard type and design customization
DEMO board, H-DMl board, other customized board, etc.
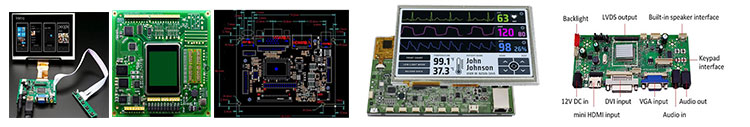
Infrared Night Vision Display Embedded Integrated Solution
UART display solution, H-DMl display solution, Window display solution, Android display solution, Raspberry Pi solution, portable secondary screen solution, etc.