As these devices become more advanced, their displays are designed to be efficient, high-performance, and user-friendly while fitting into small, compact, and flexible form factors.

Key Features of Smart Wearable Displays
1. Compact and Lightweight Design
· Small Form Factor: Smart wearable displays are typically designed to be compact and lightweight to avoid discomfort when worn. These displays need to fit into tiny spaces while offering clear, readable content.
· Flexible Displays: Many wearables use flexible OLED or AMOLED screens that can bend or curve to fit the contours of the body. This allows for better integration into wearable devices like smartwatches, AR glasses, or clothing.
· Slim Profile: Displays in wearable devices are designed to be as thin as possible while maintaining performance and durability.
2. High Resolution and Clarity
· High Pixel Density: Smart wearable displays are built with high pixel density to ensure crisp text and clear images on small screens. This is essential for maintaining readability, especially on devices like smartwatches or fitness trackers, where the display area is limited.
· AMOLED and OLED Technology: AMOLED and OLED screens offer deep blacks, vibrant colors, and high contrast ratios, making them ideal for wearables. These display types are power-efficient and provide excellent clarity even in outdoor settings or low-light environments.
3. Touchscreen and Interactivity
· Touch Sensitivity: Many smart wearable displays are equipped with touchscreen functionality that allows users to interact with the device through swipes, taps, and gestures.
· Multi-Touch Support: Wearables may offer multi-touch capabilities, enabling users to zoom, scroll, or switch between apps with more than one finger.
· Gesture Control: Some wearables, especially AR glasses or smart rings, may support gesture-based control, where users can interact with the display through movements of their fingers or hands.
4. High Brightness and Outdoor Visibility
· Outdoor Readability: Since many wearable devices are worn outdoors, they require high brightness levels to remain legible in direct sunlight. Displays in wearables often reach 1000 nits or higher for visibility in bright environments.
· Auto-Brightness Adjustment: Many wearables come with auto-brightness sensors that adjust the screen’s brightness based on the surrounding ambient light conditions. This helps preserve battery life while ensuring visibility in varying lighting environments.
5. Battery Efficiency
· Low Power Consumption: Smart wearable displays are designed to be power-efficient to maximize battery life. Technologies like OLED are particularly useful for this purpose since individual pixels can be turned off, reducing power consumption when displaying darker content.
· Power Management Features: Some wearable displays include battery-saving modes, where the screen dims or switches to a simpler display (like an analog watch face) to conserve energy when not actively in use.
6. Always-On Display (AOD)
· Always-On Functionality: Many smartwatches and fitness trackers feature always-on displays, allowing users to view basic information (like time, heart rate, or notifications) without having to activate the screen. This feature is especially useful for quick glances, ensuring users don’t need to tap the screen to check information.
· Low Power AOD: To conserve battery, the always-on display often uses low-power modes where only essential information (e.g., time, steps, or heart rate) is shown.
7. Health and Fitness Tracking Integration
· Real-Time Data Display: Many smart wearables feature displays that show real-time health data, such as heart rate, steps taken, calories burned, sleep tracking, and more. These metrics are displayed on the screen in easy-to-read formats, often with color-coded information or graphs.
· Fitness Goals and Progress: Wearable displays often include visual representations of fitness progress, such as goal completion bars or graphs showing activity trends, making it easy for users to track their performance at a glance.
8. Augmented Reality (AR) Integration
· AR-Enabled Displays: Some wearable devices, such as AR glasses, feature transparent or semi-transparent displays that overlay digital information onto the physical world. These displays are designed to provide users with real-time contextual information, such as directions, notifications, or interactive content, while maintaining awareness of their surroundings.
· Interactive AR Features: Advanced AR wearables may feature interactive displays that allow users to engage with the augmented environment via touch, voice commands, or gesture recognition.
9. Customization and Personalization
· Watch Faces and Themes: Wearables like smartwatches allow users to customize the display with different watch faces or themes, which can show various types of information (such as time, date, weather, or fitness data) in personalized formats.
· Widgets and Shortcuts: Many wearable devices allow users to set up widgets or shortcuts on the display to quickly access preferred functions, such as heart rate monitoring, music controls, or message notifications.
10. Voice and Audio Integration
· Voice Control: Many smart wearable displays feature voice assistants (e.g., Siri, Google Assistant, or Alexa), allowing users to interact with their device using voice commands. Voice recognition can be integrated directly into the display interface or be accessed via a microphone built into the device.
· Audio Feedback: Some wearable devices offer audio feedback through a small built-in speaker or connect to Bluetooth headphones, allowing users to hear notifications or messages without needing to glance at the screen.
11. Water and Dust Resistance
· IP Ratings: Smart wearable displays are typically waterproof or water-resistant to varying degrees, with IP68 ratings being common. This means the devices can be submerged in water for a certain period or resistant to sweat, rain, and splashes.
· Durable Glass: The display is often protected with hardened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, to withstand scratches and impacts from daily use, including activities like exercise or outdoor adventures.
12. Notifications and Alerts
· Real-Time Notifications: Wearables are often designed to show incoming notifications from apps, messages, calls, or social media. The display will alert users with vibrations, icons, or short text snippets, ensuring that important updates are not missed.
· Customizable Alerts: Users can typically customize the types of notifications they receive on their wearable display, such as receiving only calls or fitness-related alerts, and adjusting vibration patterns or visual cues.
13. Connectivity and Integration
· Bluetooth and Wi-Fi: Wearable displays often integrate with smartphones and other devices through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to synchronize data and receive notifications. The display shows relevant data such as message previews, fitness stats, or app notifications, in real-time.
· Cloud Syncing: Some smart wearables sync with cloud platforms to store and analyze data, such as fitness activity or health records, which can be accessed from a mobile app or other devices.
14. Security Features
· Password Protection: Many smart wearables feature security options, such as PIN codes, passwords, or biometric authentication (fingerprint or face recognition) to ensure only the authorized user can access the device’s data and settings.
· Privacy Controls: Wearable displays also allow users to manage their privacy settings, such as controlling which data is shared with third-party apps or services.
15. Haptic Feedback
· Vibration Alerts: Many smart wearables feature haptic feedback, which provides tactile alerts through vibrations. These vibrations can notify users of incoming messages, fitness milestones, alarms, or reminders.
Applications of Smart Wearable Displays

Smartwatches:
o Displays show time, notifications, fitness data, weather, and more. Users interact with the screen to access apps, make payments, track activities, and control other connected devices.
Fitness Trackers:
o Wearable displays show real-time health data, including steps, heart rate, calories burned, sleep tracking, and progress toward fitness goals.
Smart Glasses (AR Glasses):
o Wearables like Google Glass or Microsoft HoloLens integrate transparent displays that overlay digital content (like directions, messages, or visual information) onto the real world, enhancing the user’s environment with augmented reality.
Smart Rings:
o Smart rings often feature small, discreet displays that show notifications or health data, such as heart rate or activity tracking.
Smart Clothing:
o Wearable technology embedded into clothing may feature displays that show health metrics or allow interaction with external devices through gestures or touch.
Medical Wearables:
o Displays in medical wearables such as ECG monitors or glucose trackers show real-time health data, often transmitting this information to healthcare professionals or mobile apps for monitoring and analysis.
Conclusion
Smart wearable displays offer an intuitive and interactive way to access important information while maintaining a compact and functional design. Features like high resolution, low power consumption, fitness and health tracking, and AR integration make these displays essential for enhancing the wearable experience. Whether used for fitness, communication, or augmented reality, smart wearable displays continue to evolve, offering greater performance and a richer user experience.
Smart Wearable Displa Custom LCD Solutions for Diverse Applications
Brightness from 0-3000 for perfect display effect achievement. 100% NTSC makes the vividness of the picture better and the color transition in the picture more natural.
Color Temperature is positive white at around 5500K, warm white (yellowish) at 3500K and also cool white (cold) at 6500K.
Driver circuit with sufficient voltage and current values to meet output requirements and reduce the secondary development cycle.
Heat dissipation for high-brightness products to advance design of reasonable heat dissipation structure.
Power consumption, we increase the brightness without increasing the power consumption.
Cables, Backlighting also requires cables, either through an FPC connected to the LCD's FPC and controlled through a port, or a separate cable that controls it through a connector.LED life reached the standard of 30K hours Min. 50K, 70K, 100K hours are all achievable. 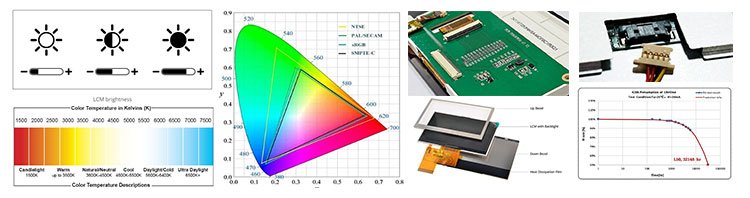
Smart Wearable Display Touch screen,standard type and customization 
Smart Wearable Display Driver board/adapter board, standard type and design customization
DEMO board, H-DMl board, other customized board, etc.
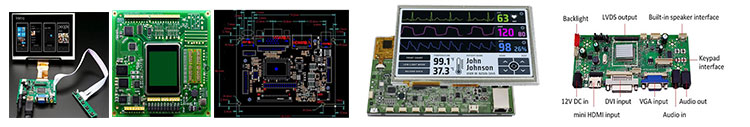
Smart Wearable Display Embedded Integrated Solution
UART display solution, H-DMl display solution, Window display solution, Android display solution, Raspberry Pi solution, portable secondary screen solution, etc.